

- #SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM HOW TO#
- #SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM FULL#
Despite measure interpretation issues, eye tracking is promising for live assessment. Yet, distinguishing visual fatigue from cognitive load with such measures is challenging due to possible links between them. The review indicates that visual fatigue can be measured with blinks and cognitive load with pupil diameter based on thirty-seven included papers. We first described visual fatigue and possible cognitive overload while learning with HMDs. We conducted this review based on five research questions.
#SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM HOW TO#
Thus, we investigate how to assess visual fatigue and cognitive load via eye tracking.

Visual fatigue and cognitive load can be measured with eye tracking, a technique that is progressively implemented in HMDs. These risks could impact learning efficiency. Risks regarding visual fatigue and high cognitive load arise while using HMDs. Virtual Reality Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) reached the consumer market and are used for learning purposes. This document sets the ground for recommendations that will be delivered in D2.2. Typically, data visualization and analytics seem to work well in VR because of these spatial information possibilities. Despite requiring higher working memory resources, such spatialization seems to promote high performance when tasks take advantage of spatial information. However, VR allows information spatialization. It appears that typical tasks transposed in VR do require more working memory resources, such as reading and writing with a keyboard. But interaction and the interface themselves could lead to mental overload because they require higher working memory resources. (3) Introducing VR as a new ICT tool requires changes in terms of interaction and interfaces and could impact mental workload. In the short term, those stressors can negatively influence work performances, and INFINITY use-case performances since stress impacts cognitive resources necessary to interact with a virtual environment and conduct investigation-related tasks (data processing, meetings, decision making etc.). Ultimately, it could describe how those stressors can become chronic through episodic exposure, feeding occupational stress. (2) Measuring the effect of several stressors related to tasks in VR should be done on the INFINITY platform. The existing literature draws guideline to ensure the user’s wellbeing and we must refer to it to develop the platform, to reduce cognitive load and improve motivation and flow at work. Even if habituation to VR, which seems to reduce side effects, has been documented, medium to long-term effects is still unknown. (1) Work in VR on the INFINITY platform should be weighted and dedicated to a limited number of tasks. Considering the current status of the technologies, the main findings can be summarized in three points: These technologies are rapidely evolving. It’s important to note that the impacts of immersive technologies on the users, their nature and intensity, closely relate to the technologies that are used. For each kind of impact, we investigated means to measure and to mitigate (for negative impact) or to strengthen (for positive impact). We consider impacts on 3 dimensions: cognition, health, and well-being. We have conducted literature analysis in the different topics and present a report of what has been previously described in various fields, including investigation activities when available. read more may occur, or control of bowel movements may be lost.This document provides an evaluation of the potential impacts of the use of immersive technologies on the users: potential positive impacts as well as potential negative impacts. Constipation Constipation in Adults Constipation is difficult or infrequent bowel movements, hard stool, or a feeling that the rectum is not totally empty after a bowel movement (incomplete evacuation). read more ) because the bladder is underactive.

People who have incomplete emptying of the bladder may have urinary frequency or urinary incontinence. Other people have difficulty emptying the bladder ( urine retention Urinary Retention Urinary retention is inability to urinate or incomplete emptying of the bladder. read more ), often because the bladder is overactive. Incontinence can occur in both men and women at any age, but it is more common among women and older people, affecting about 30% of older women. Some people pass urine involuntarily ( urinary incontinence Urinary Incontinence in Adults Urinary incontinence is involuntary loss of urine.
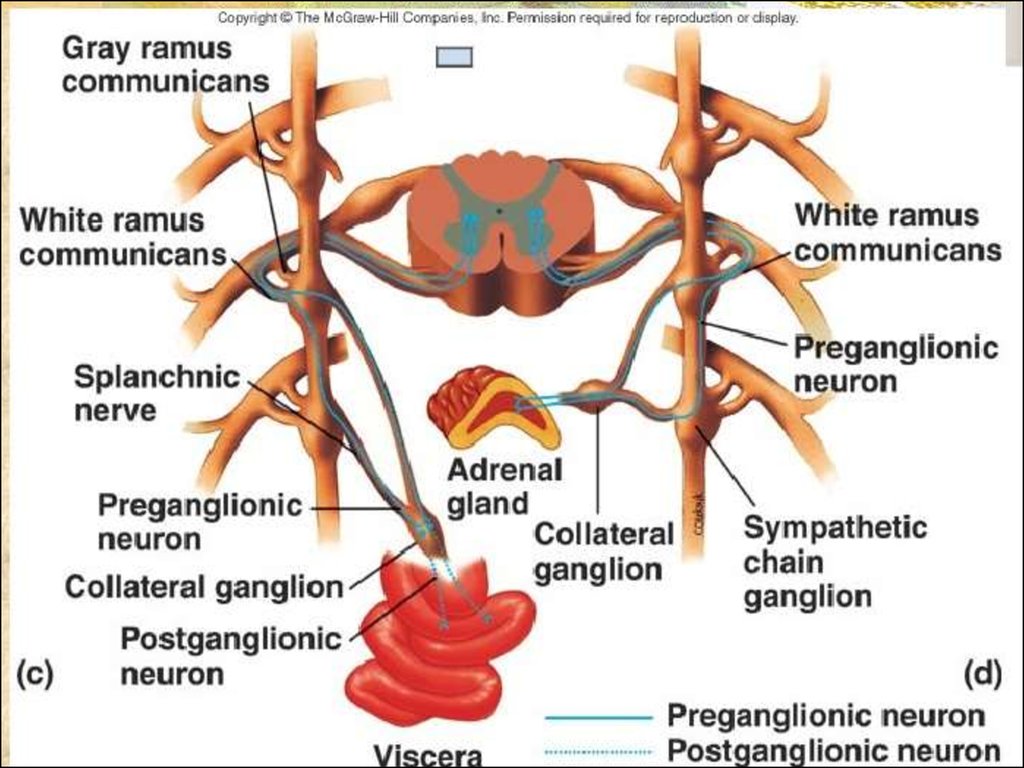
#SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM FULL#
After eating, a person with an autonomic disorder may feel prematurely full or even vomit because the stomach empties very slowly (called gastroparesis).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
